How were the different hemaglobin mutations found and differentiated?

What are the signs and symptoms, and causes of sickle cell disease?
Click above for a link to signs/symptoms/causes of sicle cell disease!
The symptoms of sickle cell disease usually shows up after an
infant is approximately four months old. Anemia is one sign of sickle cell disease. Red blood cells usually live for 120 days
before they need to be replaced by new ones. However, sickle cells die off after ten to twenty days. Another major symptom of sickle cell anemia is episodes of pain. The pain
develops because sickle-shaped red blood cells block the flow through tiny blood vessels to your abdomen, joints, and chest.
These episodes of pain that occur periodically are called crises. Some patients diagnosed with sickle cell anemia only
experience pain a few times in a year; whereas, others can experience various amounts of crises a year. Sometimes if the pain is severe, patients may be hospitalized. The pain can also occur in the bones as well.
To continue, hand-foot syndrome is another symptom of sickle cell disease. Usually a patient will have swollen
hands and feet. The swelling is caused by the sickle-shaped red blood cells blocking the blood flow in their hands and feet.
Frequent infections are also another symptom that may occur in a patient who has a sickle cell disease. Sickle cells damage
the spleen and other vital organs that fight infections. Delayed growth can be a sign of sickle cell disease as well. When a
shortage of red blood cells occurs, slow growth is affected in infants and children. A shortage in red blood cell can also delay puberty.
Lastly, vision problems may occur when a person has sickle cell disease. This occurs because tiny blood vessels supply if an individual's eyes become plugged with sickle cells, and damage the retina. Sickle cell disease is caused by a gene mutation that tells your body to make hemoglobin. The defective gene in sickle cell affects the gene that codes for the beta chain of adult hemoglobin.
In the 1950's, Hunt and Ingram sought out to investigate the basis for the differences in two types of globin. When hemoglobin protein was first separated, only the chains of Hb-A and Hb-S were different.
Each of the chains were 146 amino acids in length. By this time, enzymes that digest proteins by breaking peptide bonds had been found, and shown to recognize specific cutting sites.
When beta-globin samples from Hb-A and Hb-S were digested, the fragments that were produced were spotted in to a filter paper and fingerprinted by separation in two directions. Separation in one direction used electric current and the other used chromatography.
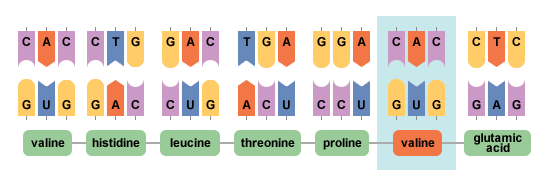
When the fragments were stained for viewing, both the samples had 30 spots, 29 that were identical to one another. Hunt and Ingram found that the unique beta globin fragment from the Hb-A had the sequence Val-his-leu-thr-pro-glu-glu- while that from sickle cell anemia was Val-his-leu-thr-pro-val-glu-.
Sickle cell disease is a point mutation because only a few nucleotides in the genes sequence had been affected.
Causes, Signs, and Symptoms
References
SCD. (n.d.). SCD. Retrieved April 28, 2014, from http://3.bp.blogspot.com/-5la80eSaL9U/TVjamNY2PyI
SCD. (n.d.). SCD. Retrieved April 28, 2014, from http://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/higher/biology

